Submitted by Yolibeth López ... on Wed, 25/05/2022 - 12:08
Congratulations to Kyle Reid, 2019 cohort PhD student on the BBSRC DTP programme, for publishing the Research Article ‘Brain Cells Release Calreticulin That Attracts and Activates Microglia, and Inhibits Amyloid Beta Aggregation and Neurotoxicity’ in Frontiers in Immunology.
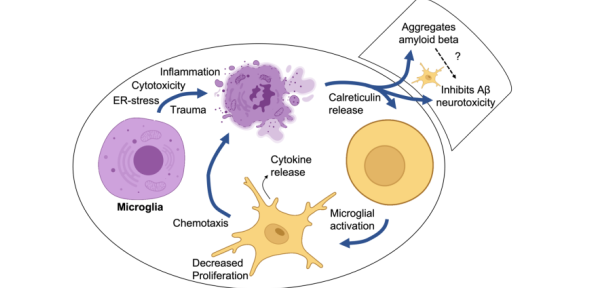
Here, Kyle and colleagues show that the protein calreticulin is released by microglia and neurons in the brain, and acts: as an alarmin to recruit and activate microglia, as an extracellular chaperone to prevent Aβ aggregation, and as a neuroprotectant against Aβ neurotoxicity.
Abstract:
Calreticulin is a chaperone, normally found in the endoplasmic reticulum, but can be released by macrophages into the extracellular medium. It is also found in cerebrospinal fluid bound to amyloid beta (Aβ). We investigated whether brain cells release calreticulin, and whether extracellular calreticulin had any effects on microglia and neurons relevant to neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. We found that microglia release nanomolar levels of calreticulin when inflammatory-activated with lipopolysaccharide, when endoplasmic reticulum stress was induced by tunicamycin, or when cell death was induced by staurosporine, and that neurons release calreticulin when crushed. Addition of nanomolar levels of extracellular calreticulin was found to chemoattract microglia, and activate microglia to release cytokines TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β, as well as chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2. Calreticulin blocked Aβ fibrillization and modified Aβ oligomerization, as measured by thioflavin T fluorescence and transmission electron microscopy. Extracellular calreticulin also altered microglial morphology and proliferation, and prevented Aβ-induced neuronal loss in primary neuron-glial cultures. Thus, calreticulin is released by microglia and neurons, and acts: as an alarmin to recruit and activate microglia, as an extracellular chaperone to prevent Aβ aggregation, and as a neuroprotectant against Aβ neurotoxicity.
To read the full publication, please click here
Reid, K.M. et al. (2022). Brain Cells Release Calreticulin That Attracts and Activates Microglia, and Inhibits Amyloid Beta Aggregation and Neurotoxicity. Front Immunol., 13 (859686): pp. 1-12.


